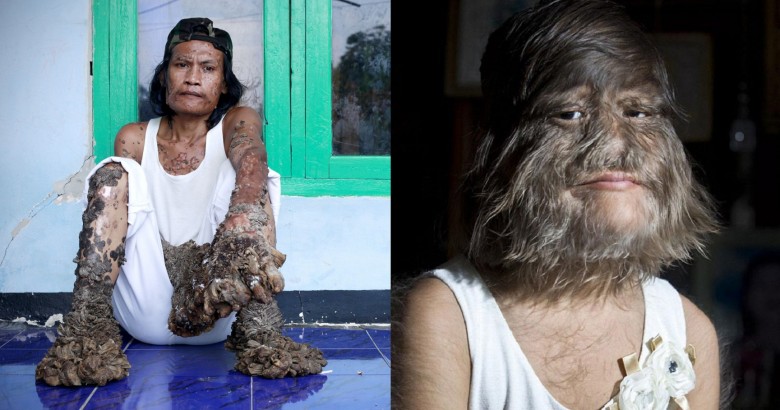
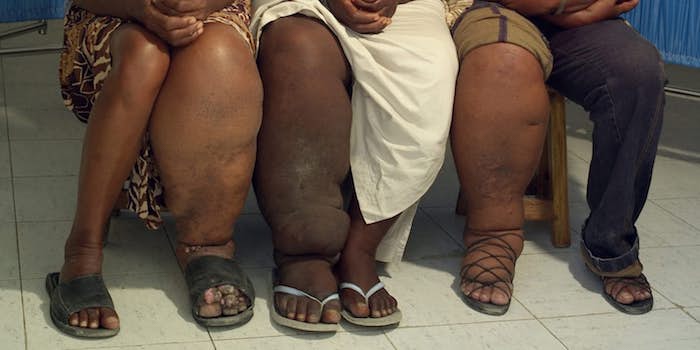
7. Elephantiasis
Also known as Lymphatic filariasis, Elephantiasis is caused by parasitic worms. It is not uncommon for cases of this disease to exist without symptoms, but some people develop large amounts of swelling of the arms, legs, or genitals. Over 120 million people worldwide are infected, with about 40 million disfigured and incapacitated by the disease. Infection is most commonly transmitted through mosquitoes that are carrying filarial parasites, though the painful swelling will not occur until later in the victim’s life.
There is no cure for Elephantiasis, the best results coming from preventive measures done by each individual community, as there are varying forms of the disease based on location. Vigorous cleaning as well as chemotherapy has proven to be effective treatments, as well as some surgeries for genital infection. As of 2015, the Ministry of Health has given up on searching for a vaccine and instead has chosen to focus on mass drug administration in areas where the worms are discovered in hopes of preventing further infection.



































Discussion about this post